DEFINITION
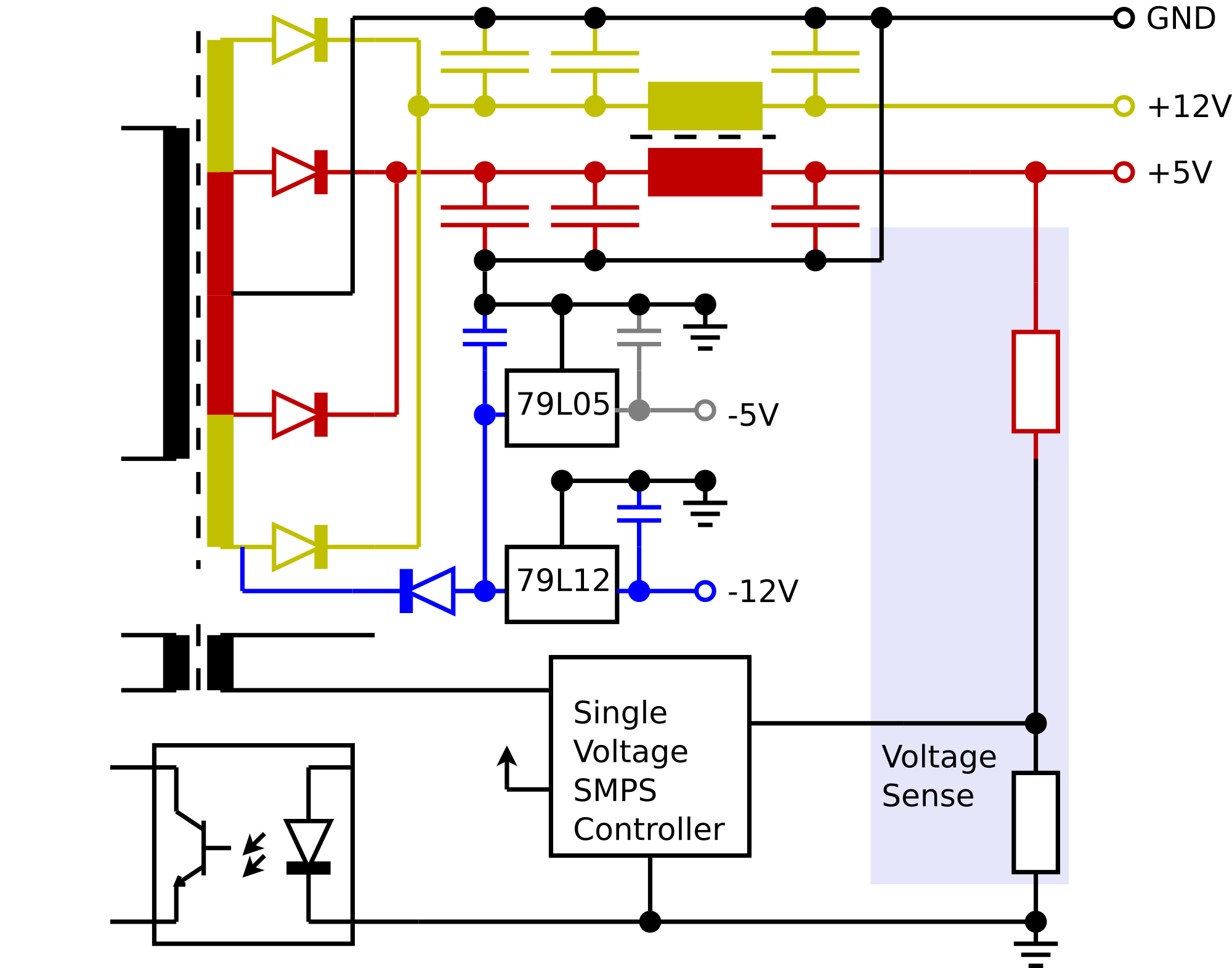
A Power Supply Unit (PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer. Modern personal computers universally use switched-mode power supplies. Some power supplies have a manual switch for selecting input voltage, while others automatically adapt to the mains voltage.
Most modern desktop personal computer power supplies conform to the ATX specification, which includes form factor and voltage tolerances. While an ATX power supply is connected to the mains supply, it always provides a 5 V standby (5VSB) voltage so that the standby functions on the computer and certain peripherals are powered. ATX power supplies are turned on and off by a signal from the motherboard. They also provide a signal to the motherboard to indicate when the DC voltages are in spec, so that the computer is able to safely power up and boot.
FUNCTION
The function of power unit is to convert the electrical power (AC) comes from wall socket to a suitable type and voltage (DC) so that each component of a computer works properly. Luck of proper supply of power will damage a computer system. The power supply receives 120 or 230V and converts into 3.3V, 5.5V and 12V. Why different converted power? That is because all components of a computer system don’t need the same power. For example, motherboard and cards use 3.3V. The most power demand parts such as Fan and drives need 12V to operate.
THE SENTENCE : I have a power supply unit (psu) with 500watt pure power. i use my PSU to my computer. without PSU my computer can't work.